A research team from Guangxi University (GXU) focusing on Quantum Information and Quantum Communication has recently made significant advances in building high-efficiency quantum digital signature networks using chip integration. Their findings were published in the international optics journal Light: Science & Applications, in a paper titled Chip-integrated quantum signature network over 200 km. The lead author of the study is Du Yongqiang, a doctoral student admitted in 2022 at the GXU School of Physical Science and Technology. Contributing authors include Li Binghong and Cao Xiaoyu, both Ph.D. candidates at the School of Physics at Nanjing University, as well as Hua Xin from the National Optoelectronics. Innovation Center. The corresponding authors are Professor Wei Kejin from GXU, Associate Professor Yin Hualei from Renmin University of China, and Xiao Xi, General Manager of the National Optoelectronics. Innovation Center. GXU is credited as both the primary and corresponding institution for this publication.

As quantum computing threatens to undermine traditional encryption methods, quantum communication is drawing increased attention for its inherent advantages in securing information. Among these, QDS stands out as a key cryptographic technique that ensures message integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation — crucial features for applications in e-commerce, digital currencies, and blockchain technologies. QDS has progressed swiftly from early proofs of concept to fully functional system-level demonstrations, positioning it as a strong candidate for future commercial quantum cryptography. However, existing QDS systems have relied heavily on complex and costly fiber-optic setups, limiting their scalability and compatibility with today’s communication networks. This makes the development of chip-integrated QDS networks — which offer lower cost, higher efficiency, and better scalability — a research direction with strong potential for real-world deployment.
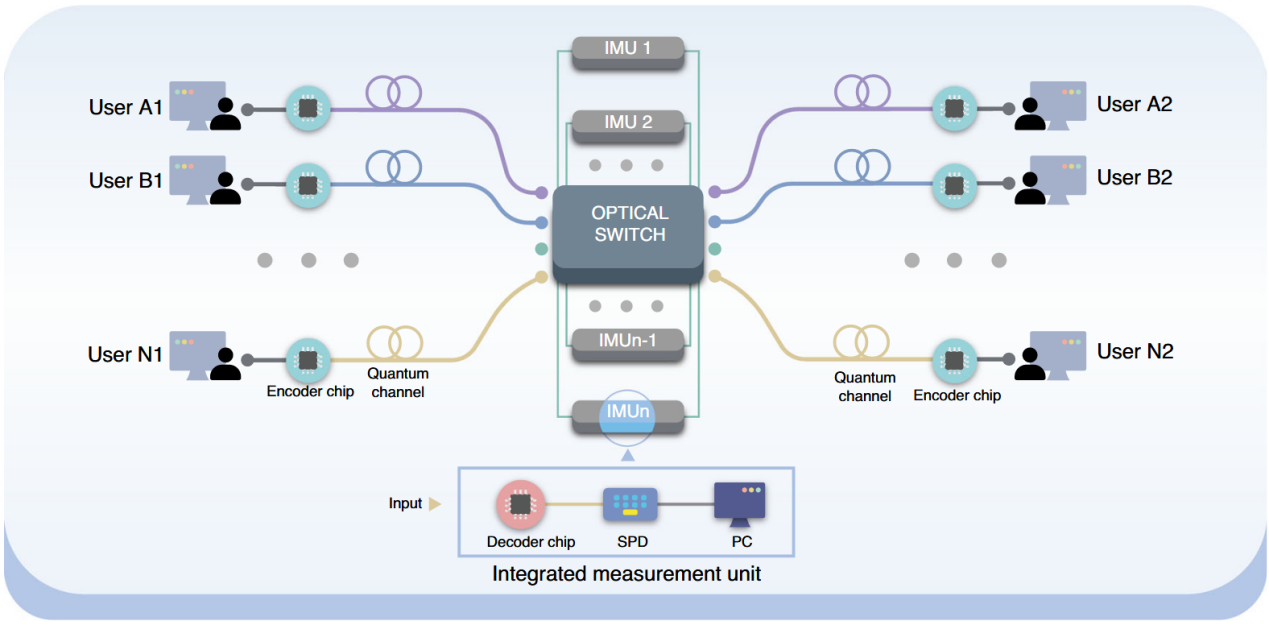
Figure 1. Diagram of the chip-integrated QDS network using a star-shaped topology.
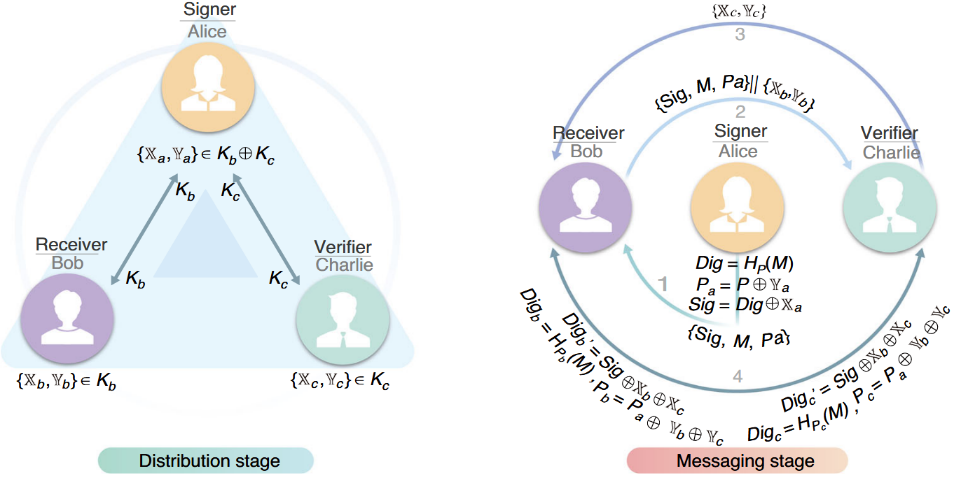
Figure 2. Operational schematic of the efficient QDS protocol.
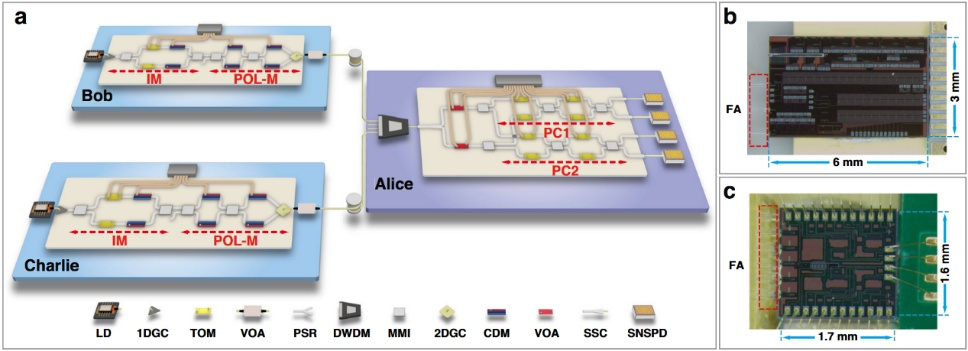
Figure 3. Experimental configuration. (a) Three-node quantum network built on integrated chips. (b) Microscopic view of the silicon-based encoder chip. (c) Microscopic view of the silicon-based decoder chip.
To address this challenge, the Quantum Information and Quantum Communication team at GXU, in collaboration with Xiao Xi’s group at the National Optoelectronics Innovation Center, leveraged prior expertise in several core technologies — including polarization-encoded quantum key distribution decoders with polarization tracking, resource-efficient chip-based QKD systems, and chip-integrated source-independent quantum random number generators. Working together with Associate Professor Yin Hualei’s team from Renmin University of China, they introduced an innovative star-shaped QDS network architecture (Figure 1) and designed a new protocol: the single decoy-state, one-time global hash QDS (Figure 2). This protocol not only enhances overall system performance but also greatly simplifies both the hardware setup and the data post-processing workload. Using silicon-based encoder and decoder chips, they successfully demonstrated a three-node QDS network prototype.
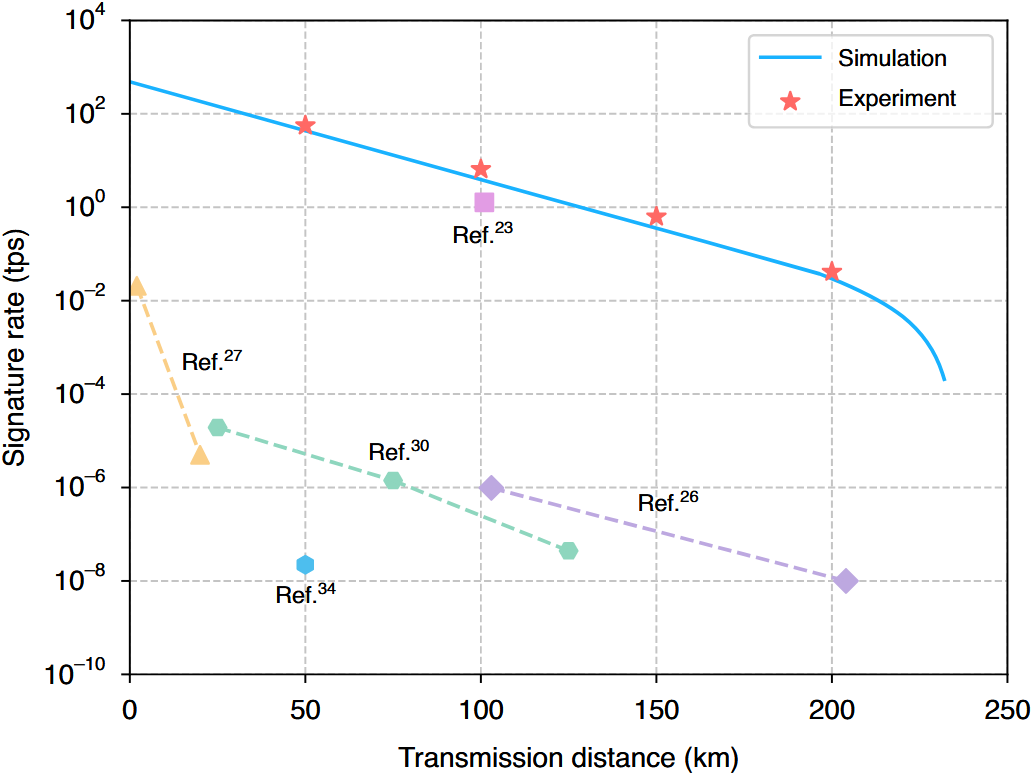
Figure 4. Measured signature rates across various transmission distances.
Using the proposed network design and a newly developed QDS protocol, the research team carried out a series of experiments at varying transmission distances. The results highlight key advances achieved in this study. In particular, the chip-based QDS system was able to sign a 1 Mbit file at a rate of 0.04 signatures per second over a 200-kilometer optical fiber link. This work represents a meaningful step toward the real-world application of QDS and holds promise for broader use in areas such as quantum e-commerce and quantum blockchain.
Light: Science & Applications, launched in 2012, is an international journal focused on cutting-edge developments in photonics and optoelectronics. It emphasizes interdisciplinary breakthroughs involving materials science, life sciences, and quantum technologies, and publishes original research, comprehensive reviews, and forward-thinking perspectives that have the potential for major theoretical or technological impact.