At 12:12 on May 17th, the CXPD (Cosmic X-ray Polarization Detection) 02 CubeSat, developed under the leadership of Guangxi University, was successfully launched aboard the Zhuque-2 (Vermilion Bird-2) modified Yao-2 carrier rocket from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center and entered its planned orbit smoothly. As a full-scale engineering prototype of the Low-energy Polarization Detector (LPD) for the POLAR-2 project on China’s space station, the satellite will conduct in-flight validation for X-ray polarization sky surveys of transient sources such as gamma-ray bursts.
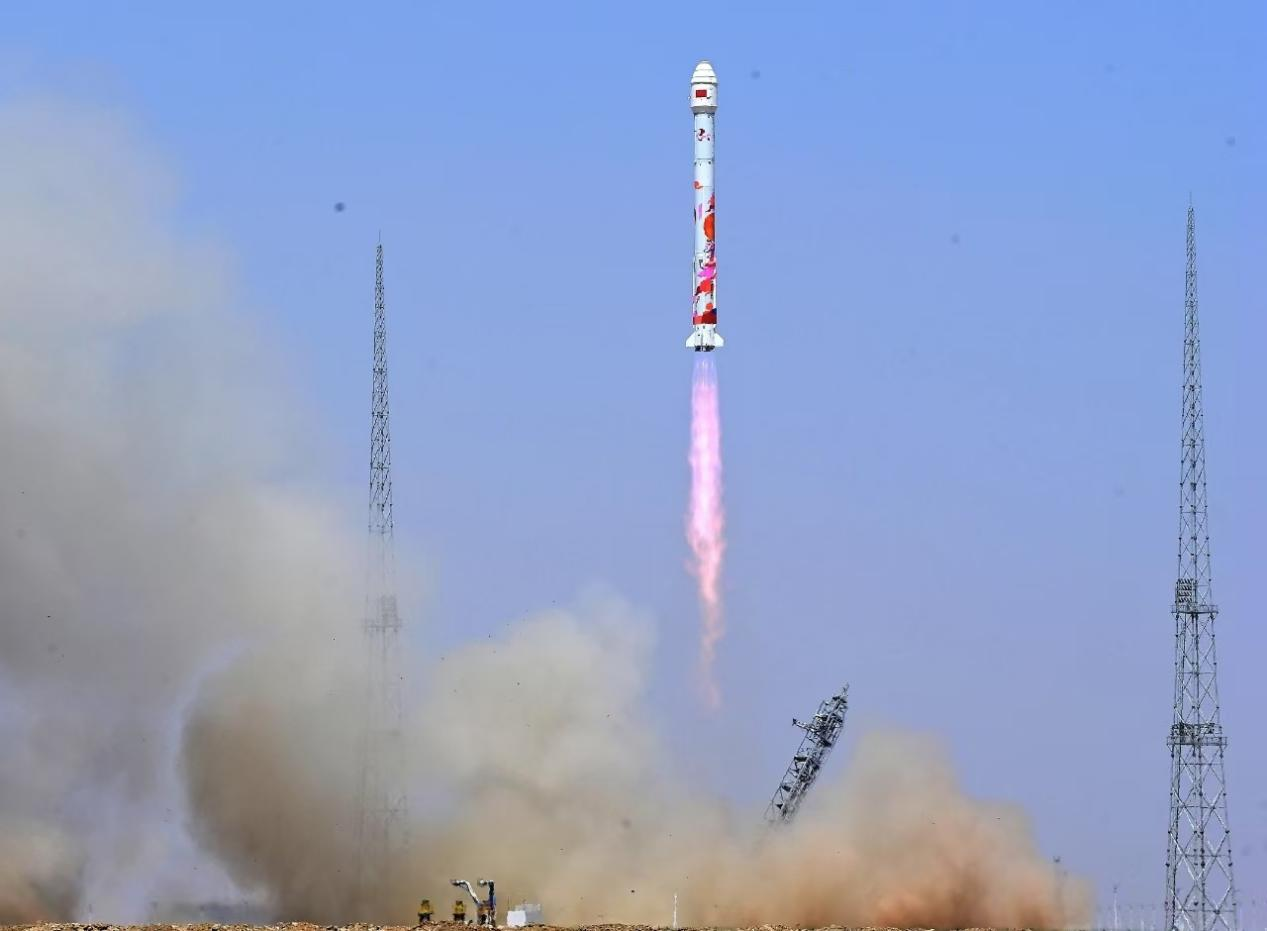

It is reported that the CXPD-03 and CXPD-04 CubeSats, also developed under the leadership of GXU, were successfully launched from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on May 14. As the scientific payload of the "Tri-Computing Constellation" – the inaugural satellite cluster of Zhejiang Lab – these satellites will leverage an independently developed space-based astronomical AI model to conduct on-orbit rapid detection, identification, and classification of transient sources such as gamma-ray bursts (GRBs). Additionally, they will initiate dual-satellite collaborative observations, establishing an AI-powered, spaceborne computing and multi-satellite coordinated observation paradigm for astronomical transients.
The CXPD-02, 03, and 04 CubeSats were developed by the School of Physical Science and Engineering at Guangxi University, in partnership with Central China Normal University, the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (UCAS), and the Institute of High Energy Physics (IHEP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The project overcame multiple technological challenges, achieving full-chain independent R&D—from core components to intelligent satellite systems—all autonomously developed in China.

 Home
>
News & Events
>
News
Home
>
News & Events
>
News
 Home
>
News & Events
>
News
Home
>
News & Events
>
News